Launching and growing a business involves more than a great idea and market demand. Business law shapes how companies are formed, operated, protected, and scaled. Entrepreneurs who understand legal fundamentals are better equipped to avoid disputes, manage risk, and build sustainable ventures.
This guide outlines the core business law essentials every entrepreneur should know, explained clearly and practically.
Choosing the Right Business Structure
Selecting a business structure is one of the earliest and most important legal decisions you will make. The structure affects liability, taxes, management control, and compliance obligations.
Common structures include:
- Sole Proprietorship – Simple to form, but no separation between personal and business liability
- Partnership – Shared ownership with joint legal responsibilities
- Limited Liability Company (LLC) – Offers liability protection with flexible management
- Corporation – Separate legal entity with strong liability protection and formal governance
Choosing the right structure early helps prevent legal exposure and tax complications later.
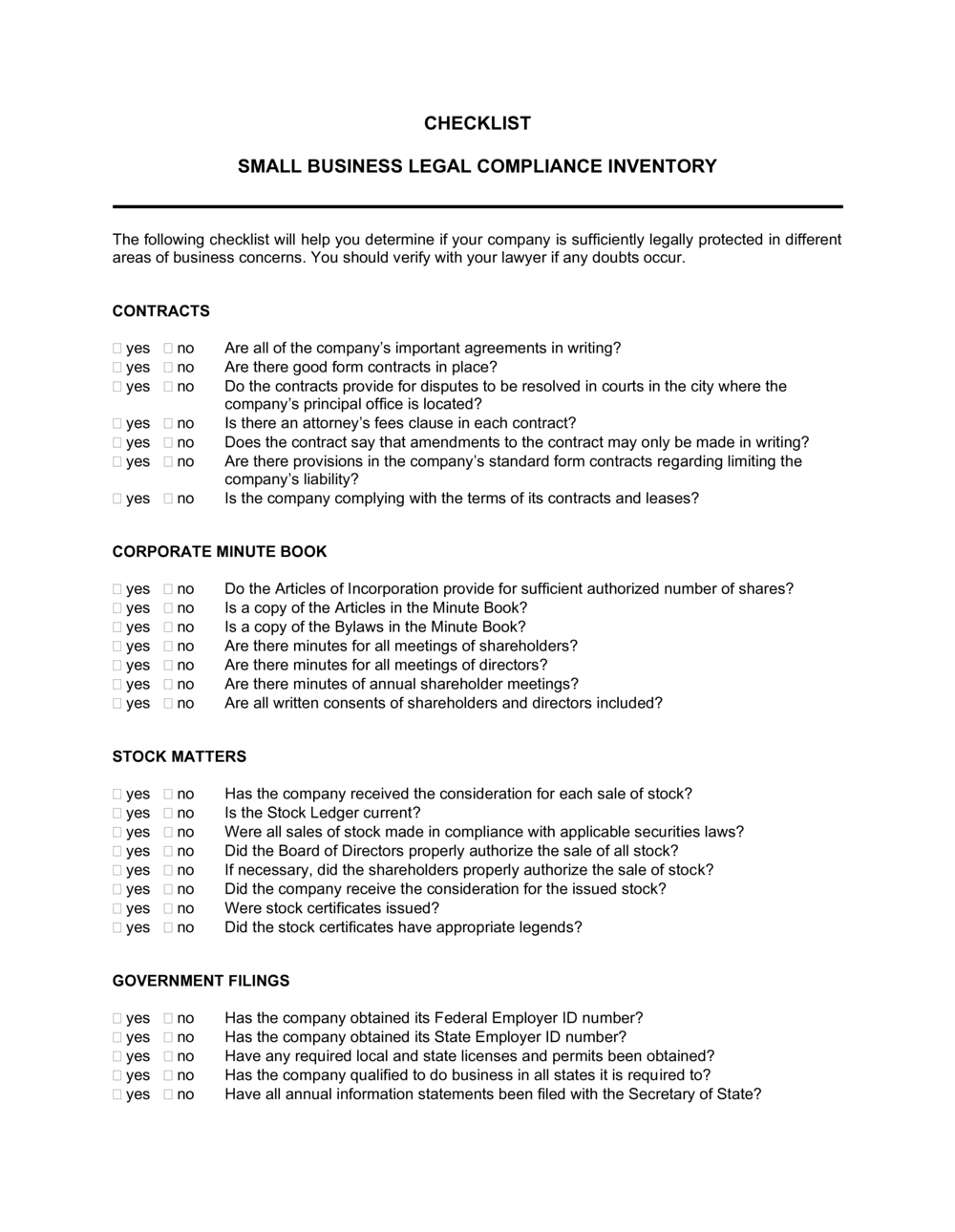
Business Registration and Compliance
Every business must meet certain registration and compliance requirements to operate legally.
Key legal steps include:
- Registering the business name
- Obtaining required licenses and permits
- Registering for taxes at local, state, and federal levels
- Complying with zoning and industry regulations
Failure to comply can result in fines, shutdowns, or legal disputes that disrupt operations.
Contracts and Agreements
Contracts are the backbone of business relationships. Clear, enforceable agreements reduce misunderstandings and protect all parties involved.
Entrepreneurs should prioritize written contracts for:
- Client and customer agreements
- Vendor and supplier relationships
- Partnership and shareholder arrangements
- Independent contractor and consultant services
Well-drafted contracts define expectations, payment terms, dispute resolution methods, and exit rights.
Employment and Labor Law Basics
Hiring employees introduces a range of legal obligations. Missteps in employment law can be costly and damaging.
Key areas to understand include:
- Wage and hour requirements
- Employee classification versus independent contractors
- Workplace safety standards
- Anti-discrimination and harassment laws
- Termination and severance practices
Even small teams must comply with labor laws to avoid legal exposure.
Intellectual Property Protection
Your ideas, brand, and creative assets often represent significant business value. Intellectual property (IP) laws help protect those assets from misuse.
Entrepreneurs should consider protection for:
- Business names and logos through trademarks
- Original content, software, and designs through copyrights
- Inventions or processes through patents
- Confidential information through non-disclosure agreements
Protecting IP early strengthens brand identity and competitive advantage.
Managing Business Risk and Liability
Legal risk is inevitable, but it can be managed with proper planning.
Risk management strategies include:
- Maintaining adequate business insurance
- Separating personal and business finances
- Following corporate formalities
- Keeping accurate financial and legal records
These practices help preserve liability protection and reduce exposure to lawsuits.
Dispute Resolution and Legal Preparedness
Disputes may arise with customers, partners, employees, or competitors. How they are handled can determine long-term business stability.
Entrepreneurs should:
- Include dispute resolution clauses in contracts
- Understand mediation and arbitration options
- Address conflicts early before escalation
- Maintain documentation to support legal positions
Preparation minimizes disruption and protects business continuity.

Why Legal Awareness Matters for Growth
As businesses grow, legal complexity increases. New markets, employees, investors, and partnerships introduce additional regulations and responsibilities.
Strong legal foundations help entrepreneurs:
- Scale with confidence
- Attract investors and partners
- Avoid costly compliance failures
- Focus on innovation instead of litigation
Legal awareness is not about fear—it is about control and long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a lawyer to start a small business?
While not legally required, legal guidance can help prevent mistakes related to structure, contracts, and compliance.
Can I change my business structure later?
Yes, many businesses evolve their structure as they grow, though changes may involve tax and legal implications.
What contracts should every entrepreneur have?
At minimum, customer agreements, vendor contracts, and confidentiality agreements are strongly recommended.
How can I protect my business name?
Registering a trademark provides stronger protection than name registration alone.
What legal risks do online businesses face?
Online businesses must address data privacy, consumer protection laws, and intellectual property compliance.
How often should I review my legal documents?
Documents should be reviewed regularly, especially during growth, funding, or operational changes.
Is insurance enough to protect my business legally?
Insurance is important, but it does not replace proper legal structure, contracts, and compliance.
Understanding business law essentials empowers entrepreneurs to make informed decisions, protect their ventures, and build businesses that are legally sound and positioned for long-term growth.

